How to Identify Amanita Muscaria Safely: Foraging and Preparation Tips
Introduction: The Psychedelic Fairy Tale Mushroom Making a Modern Comeback
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of interest in natural remedies and traditional ethnobotanical wisdom. Among these fascinating treasures from nature is the iconic Amanita muscaria mushroom, often instantly recognized by its bright red cap adorned with white warts. Despite its fairy-tale appearance, Amanita muscaria has a controversial and complex reputation, owing to its psychoactive compounds and traditional uses by indigenous cultures.
Known commonly as the fly agaric, Amanita muscaria has been used for centuries in Siberian shamanic practices and is currently being reevaluated in modern wellness and mental health communities. While not classified as a classic psychedelic in the same class as psilocybin mushrooms, Amanita muscaria contains unique compounds such as muscimol and ibotenic acid that interact with the GABAergic system rather than serotonergic receptors. This distinct mechanism has sparked interest in its therapeutic potential for conditions such as anxiety, insomnia, inflammation, and certain neurological disorders.
However, the use of Amanita muscaria comes with genuine safety concerns. The mushroom contains toxic compounds and must be properly identified and carefully prepared to mitigate potential adverse effects. Foraging without adequate knowledge can lead to confusion with both edible and deadly look-alikes, increasing the risk of toxic ingestion.
The Science Behind Amanita Muscaria: A Unique Psychoactive Profile
Understanding Amanita muscaria‘s medical relevance requires distinguishing myth from evidence-based science. One of the key psychoactive components of the mushroom is muscimol, a powerful GABA-A receptor agonist. Unlike psilocybin, muscimol induces sedative and dissociative effects rather than visual hallucinations. This different pharmacological pathway is the basis of ongoing investigations into its potential therapeutic uses.
A 2022 study published in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology discussed muscimol’s impact on the central nervous system and its potential as an anxiolytic and sleep aid when dosed appropriately. The researchers found preliminary evidence to support its utility in reducing anxiety and improving sleep due to its modulation of GABAergic neurotransmission—a mechanism similar to pharmaceutical benzodiazepines but with a different risk profile. Read the full study
Another trial published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology focused on the traditional use of Amanita muscaria by Siberian tribes, documenting both spiritual and therapeutic applications. These practices involved drying the mushroom to reduce its toxicity—specifically, transforming ibotenic acid (a more toxic compound) into the milder and more beneficial muscimol. Explore the research
How to Identify Amanita Muscaria in the Wild (And Avoid Dangerous Look-Alikes)
Despite its promising attributes, misidentification and improper preparation remain significant barriers to safe use. Amanita muscaria must never be eaten raw, as ibotenic acid in fresh mushrooms can cause vomiting, confusion, or seizures.
When foraging, keep an eye out for these clear features:
– Cap: Bright red (though can fade to orange or yellow), with signature white warts
– Gills: White and free from the stem
– Stem (Stipe): White, with a skirt-like ring near the top
– Base: A swollen bulb or volva at the bottom
– Habitat: Often found under birch, pine, and spruce trees, especially in temperate forests of the Northern Hemisphere
Also beware of mushrooms that slightly resemble Amanita muscaria but are actually toxic, such as Amanita pantherina (panther cap) or even some deadly Amanitas like Amanita phalloides (death cap). Clarity in identification is essential, and mushroom ID apps or AI tools can be a helpful starting point—but they should never replace experienced guidance.
Learning through reputable sources like illustrated field guides or local mycology clubs can dramatically reduce the risk of misidentification.
Preparing Amanita Muscaria Safely: From Toxic to Therapeutic
Proper preparation is as important as accurate identification. Consuming raw Amanita muscaria can expose you to neurotoxic levels of ibotenic acid, which may cause intense nausea, dizziness, delusions, or convulsions.
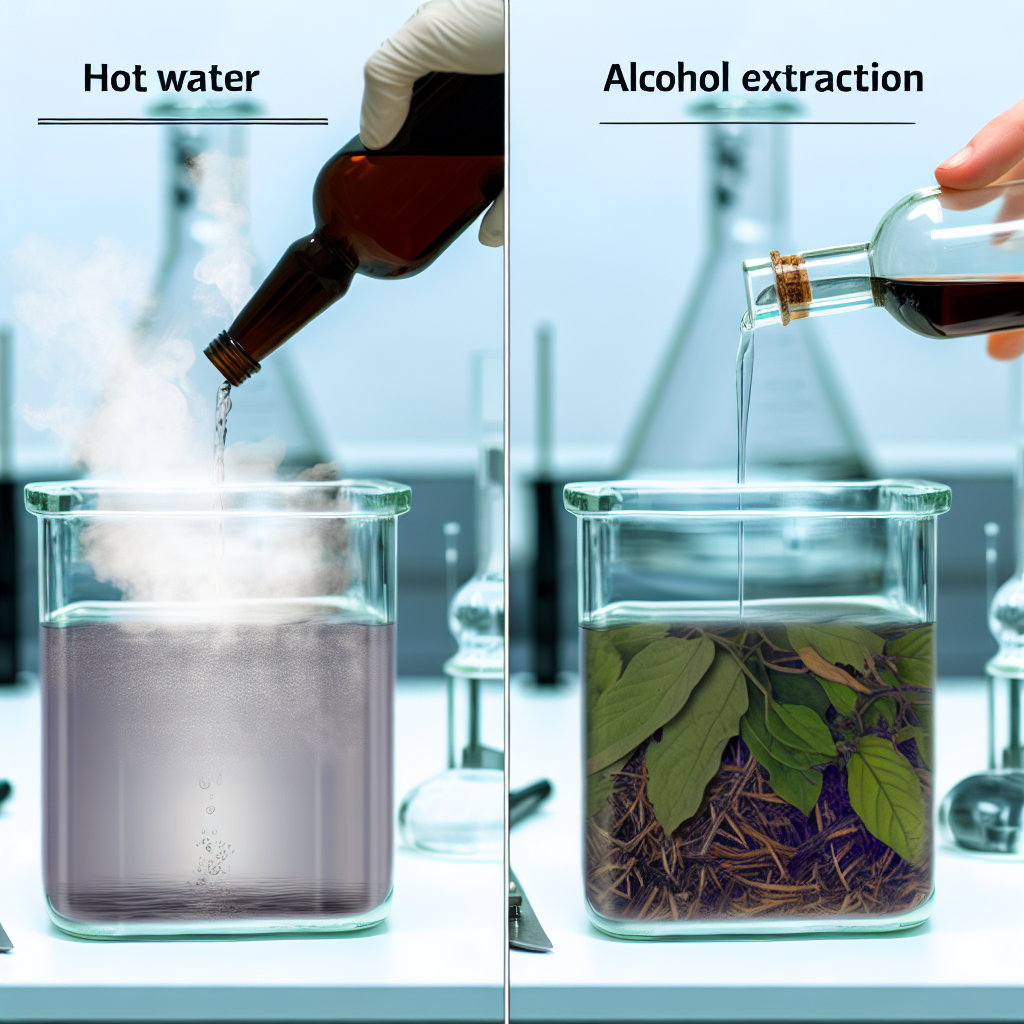
The safest way to prepare Amanita muscaria is by drying, which decarboxylates the ibotenic acid into muscimol, making it considerably less toxic.
Drying Tips:
1. Slice caps thinly to allow even drying
2. Use a dehydrator or an oven set to 150°F–170°F (65°C–75°C)
3. Allow 12–24 hours of drying, depending on thickness and humidity
4. Store in airtight containers in a cool, dry place
Some traditional users will then steep the dried mushroom in hot water or milk, or create tinctures or topical solutions, depending on the intended use.
Always begin with very small amounts and wait several hours to assess your body’s response before increasing. As with any natural remedy, individual reactions can vary significantly.
Modern Research and Ancient Roots: What Science Says About Amanita Muscaria
As scientific interest in Amanita muscaria‘s therapeutic profile grows, researchers are exploring its relevance in areas like integrative medicine, neurology, and chronic illness management.
Some proposed therapeutic effects of muscimol include:
– Anxiety relief
– Improved sleep
– Muscle relaxation and anti-inflammatory action
– Neuroprotective effects in degenerative conditions
However, these benefits are still being studied, and dosage, bioavailability, and long-term safety must be rigorously validated.
Just as Siberian shamans once stewarded the delicate balance between dose and ritual, today’s users must approach this mushroom with informed caution and reverence.
Final Thoughts: Rediscovering Ancient Wisdom Through Responsible Wellness
Amanita muscaria continues to capture the curiosity of modern foragers and natural health enthusiasts thanks to its cultural history and emerging therapeutic potential. However, with beauty comes risk—proper identification, responsible harvesting, and safe preparation are essential steps toward mindful use.
As science deepens our understanding of this unique mushroom, an informed and cautious approach can open doors to ancient healing practices reimagined for contemporary wellness.
Whether you are a curious forager, natural medicine seeker, or advocate of integrative healthcare, the key to safely exploring Amanita muscaria lies in education, patience, and respect for nature’s potent medicines.
References
– Frontiers in Pharmacology (2022). “The pharmacological properties of muscimol and its potential therapeutic applications.”
– Journal of Ethnopharmacology (2020). “Traditional use of Amanita muscaria in indigenous cultures.”
– North American Mycological Association. “Mushroom Poisoning Syndromes.”
Concise Summary:
Amanita muscaria, the iconic red-capped mushroom, has gained renewed interest for its potential therapeutic benefits, such as anxiety relief and improved sleep. However, this mushroom also contains toxic compounds and must be properly identified and prepared to mitigate risks. This article explores the science behind Amanita muscaria, provides tips for safe foraging and preparation, and discusses the emerging research on its medical applications.

Dominic E. is a passionate filmmaker navigating the exciting intersection of art and science. By day, he delves into the complexities of the human body as a full-time medical writer, meticulously translating intricate medical concepts into accessible and engaging narratives. By night, he explores the boundless realm of cinematic storytelling, crafting narratives that evoke emotion and challenge perspectives. Film Student and Full-time Medical Writer for ContentVendor.com